Algae are chlorophyll-bearing autotrophic members of thallophytes comprising a large heterogeneous assemblage of relatively simple plants.
Algae may be aquatic, semi-aquatic, or terrestrial in their habitat. In the sea, they make up the major part of the vegetation. On pools of calm water, they often form the green-colored “pond screen” or “pond scum”.

Types of Algal Habitat
Algae are found everywhere on the earth, in air, water, and soil. Three types of algae can be found based on their habitats.
- Terrestrial Algae
- Aquatic Algae
- Algae as of Unusual Habitats
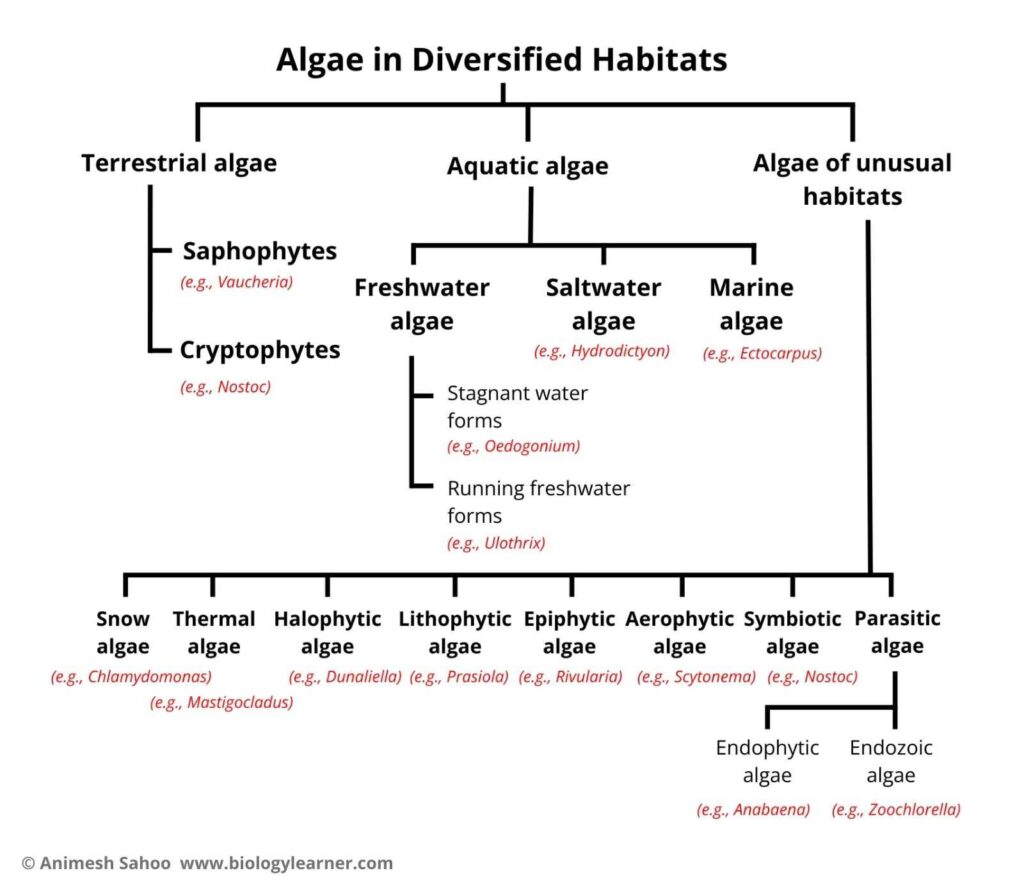
Terrestrial Algae
Terrestrial algae are also known as edaphophytes. The edaphophytes are found upon or inside of the earth. They occur on moist soil as a part of soil flora, and also on barks of trees, on damp wood, on rocks and cliffs, etc.
Terrestrial algae are two types: Saphophytes and Cryptophytes.
Saphophytes
Saphophytes are surface algae found on soil. Fritschiella, Botrydium, and Vaucheria of Myxophyceae are found as saphophytes and they occur upon the surface of the soil.
Cryptophytes
Cryptophytes are subterranean blue-green algae found inside the soil.
Subterranean blue green algae are Anabaena and Nostoc.
Aquatic Algae
They are found in all types of water. Algae can be growing even in small trenches, ponds big rivers, and oceans. Aquatic algae can be grouped into the following three sub-groups:
- Freshwater algae
- Saltwater algae
- Marine algae
Freshwater Habitat of Algae
A large number of algae are found in freshwater. They can be divided into two types: Still or stagnant water forms and Running water forms.
Still or Stagnant Water Forms
Mostly, members of myxophyceae and Chlorophyceae develop in stagnant water. Common examples of them are Zygnema and Oedogonium.
Chara is found at the bottom of shallow ponds and lakes. While Rivularia and Gleotrichia are common examples of myxophyceae growing in such habitats.
Running Freshwater Forms
Some algae are found in running water. In such habitats, the quality of water contains a higher amount of oxygen.
Common examples are Chladophora, Ulothrix, Vaucheria, Batrachospermum, etc.
Saltwater Habitat of Algae
In the water of saltish lakes, Hydrodictyon and Chlamydomonas, etc. are found. These algae forms are called halophytes.
Marine Algae
The algae are found in the sea. Such algae are never found in freshwater. Members of Rhodophyceae and Phaeophyceae mostly occur as marine algae, e.g. Ectocarpus, Polysiphonia, Fucus, Caulerpa, etc.
Several members of the order Siphonales also inhabit seawater.
Algae as of Unusual Habitats
Several algae are found in variable unusual habitats. They can be grouped as follows:
- Snow algae or cryophytes
- Thermal algae
- Halophytic algae
- Lithophytic algae
- Epiphytic algae
- Aerophytic algae
- Symbiotic algae
- Parasitic algae
Snow habitat of algae or Cryophytes
Commonly, it is unimaginable to think that at the peak of mountains and snow-covered rocks, algae can develop, but some species of algae grow on ice and snow.
Due to the growth of algae-Raphidonema, some mountains in Europe look absolutely green. According to Kol, the greenness of mountains may be due to Chlamydomonas, and yellowness is also. Due to the growth of snow algae, Haematococcus nivalis, the color of arctic and alpine areas becomes red.
The brownish to purple color of snow appears due to the presence of Ancyclonema nordenshioledii, while the presence of Protonema and Scotiella makes the color of snow yellowish or greenish. On snow, the genus Phormidium of Cyanophyta is also found to grow.
Kol has divided the snow algae of the Alaska mountains into the following categories:
- Algae are found in abundance in snow and produce ice bloom, e.g., Ancyclonema.
- Algae produce both snow and ice, such as Cylindrocystis and Trochiscia.
- Some algae are found on snow but do not form ice, such as Raphidonema and Chlamydomonas.
- Those algae forms are found in the form of temporary cryophytes, e.g., Gleocapsa and Phormidium.
Thermal algae
In Yellowstone National Park of America, even at the temperature of 85°C algae members are present, commonly the plants do not grow at such high temperatures, e.g., Mastigocladus and species of Phormidium.
Halophytic algae
Some members of Myxophyceae such as Dunaliella and Stephoenoptera can be found in highly saltwater. Chlamydomonas chrenbegii is found growing in the slatish water of lakes Sambhar and Crimera.
Lithophytic algae
These algal forms remain closely attached to stones and rocks. Commonly, members of the Myxophyceae like Rivularia and Gleocapsa are found growing on rocks.
Algae such as Prasiola, Vaucheria, and diatoms grow on rocks in moist and shady places.
Epiphytic algae
Quite a large number of forms are found growing on rocks or bigger algal members as epiphytes e.g., Bulbochaete, Ulothrix, Oedogonium, etc.
Batrachospermum grows in close contact with algae, like- Choloeochaete and Chaetophora, which in turn grow on the leaves of higher plants like Nelumbo, Castolia, and Vallisneria. A red alga such as Audocinella is found on mosses. Colonies of Rivularia are found growing on grass-Scirpus.
Aerophytic algae
Tiffany has kept all those algal forms under aerophytes which grow on leaves (Epiphyllophytes), on barks (Epiphloeophytes), on animals (Epizoophytes), and on rocky projecting surfaces.
Algae like Phormidium, Scytonema, Cyanoderma, and Trichophilus are found growing on the scales of animals known as sloths. Some euglenoids have been found growing on the bark.
Symbiotic habitat algae
These are a large number of algal forms which live symbiotically with plants and animals.
The presence of Nostoc in the thallus of Anthoceros, Anabaena cycadae in the coralloid roots of Cycas, and Anabaena inside Azolla are good examples of such a symbiotic relationship. The best example is lichen thallus, in which algae and fungi live together. Chlorella and Azotobacter chroococcum (a nitrogen-fixing bacteria) are other outstanding examples of symbiosis.
The presence of Cladophora on snails and Zoochlorella within Hydra is an example of symbiosis with animals. According to Gelei, in the mucus of the frog Rana agile, Trochiscia is found. Oedogonium undulatum has been described to be found in association with the larva of Crustaceans and other insects.
Parasitic habitat algae
Some algae are parasitic in nature. Cephaleuros, a member of the Chlorophyceae, develops as a partial parasite on tea, coffee, and black pepper.
Several members(red algae) of the Rhodophyceae, those algal forms which live inside various types of plants and animals, are called endobiotics, and, from the point of view of convenience, they can be divided into endophytic and endozoic.
- Endophytic: They are found in various plant parts, such as Nostoc in Anthoceros’ thallus, Anabaena in Cycas’ coralloid root, and Azolla’s leaves.
- Endozoic: Certain algae occur inside the bodies of animals. For instance, Zoochlorella is found inside the body of a Hydra.
