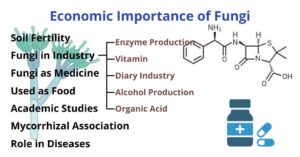
Economic Importance of Fungi
Fungi lack the chlorophyll pigment essential for independent existence. Hence, they must get their food from other living organisms or from dead or decaying organic matter. Economical fungi have great…

Fungi lack the chlorophyll pigment essential for independent existence. Hence, they must get their food from other living organisms or from dead or decaying organic matter. Economical fungi have great…
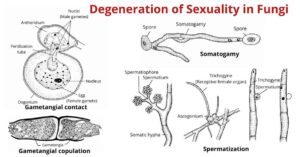
Sexuality in fungi is diverse and fascinating. In fungi, gradual degeneration of sexuality can be observed. Degeneration of sexuality means functional and structural degeneration of sex organs, leading to the…
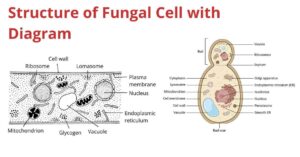
Fungi are eukaryotic, spore-bearing microorganisms. They are heterotrophic (i.e., can’t produce their own food through photosynthesis) and digest food externally by releasing hydrolytic enzymes into their surroundings. Fungi have unicellular…
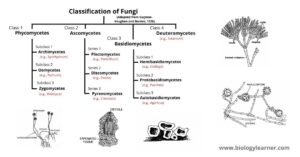
The classification of the fungi is a very challenging task since it presents various problems that originate from the differences of opinion of different workers. The situation becomes even more…

Penicillium is a saprophytic fungus of the class Plectomycetes. It is found in all parts of the world. The name penicillium is derived from the Latin word penicillus, which means…

Aspergillus is a common saprophytic fungus of the class Plectomycetes. The name Aspergillus is adapted from the Latin name Aspergillum, which means holy water sprinkler. As the fungus has a…

Peziza is a saprophytic fungus of the class Discomycetes. It is often coprophilous in habit, growing on dung. Peziza is commonly known as cup fungus, due to its cup-shaped fruit…

Ascobolus is a coprophilous fungus (i.e., it grows on animal dung) of the class Discomycetes. The genus Ascobolus was introduced in 1791 by C.H. Persoon. Occurrence of Ascobolus Ascobolus is…

Rhizopus is a saprophytic fungus of the class Zygomycetes (as it produces zygospores in the sexual reproductive phase). Its species usually occur on dead organic material. The name Rhizopus was…