The scientist R. Grant used the term phylum Porifera for the first time in 1836. Porifera belongs to the sub-kingdom Parazoa. Although all the animals in this group are multicellular, the cells that make up the body do not form tissues and organs.
In the course of evolution, they originated as a group of organisms, completely different from other multicellular organisms. The animals of Porifera are commonly called the Sponge.
The Greek word “porus= pore and ferrus= to bear”.
Definition of Porifra
Porifera are referred to as organisms that have numerous pores on the body and a distinctive canal system lined internally by choanocytes.
Characteristics of Porifera
- Most of the organisms in this phylum are marine.
- They are having numerous pores on the body. These pores are called Ostia.
- At the anterior end of the body, a large pore called the osculum is present.
- They are diploblastic.
- The canal system is present in their body.
- Flagella-associated choanocyte cells are present.
- Body without any tissue differentiation.
- The body is having an endoskeleton formed of calcareous or siliceous spicules.
- The endoskeleton may also contain spongin fibers.
- The nervous system is completely absent in the body.
- Reproduction occurs both asexually and sexually. Asexual reproduction occurs by producing gemmules and buds.
- They have lacking locomotory organelles and are sessile in habit remaining fixed with a substratum.
Porifera Identification
- Body wall: Their body wall is made up of numerous pores called Ostia.
- Movement: The animals are non-motile, and permanently attached to an object.
- Physical structure: Numerous tiny spongin fibers called spicules form the structure of the body.
- Canal system: Different types of canal systems are seen inside the body.
- Tissue system: Although they are multicellular animals, their tissue system is not formed.
Examples
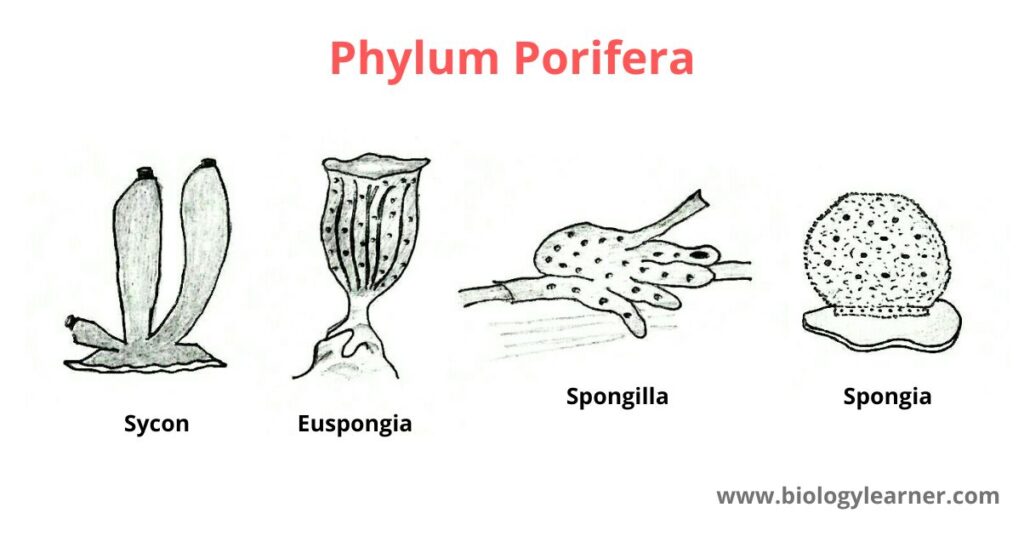
Some common animals under the phylum Porifera are Sycon, Spongilla, Enplectella, Euspongia, etc.
Porifera Classification
Phylum Porifera has been divided into three classes: Calcarea, Hexactinellida, and Demospongiae.
The classification followed here is based on Storer and Usinger (1971), a modified form of Hyman’s classification (1940).
Class 1. Calcarea
- Order 1. Homocoela (e.g., Clathrina)
- Order 2. Heterocoela (e.g., Sycon)
Class 2. Hexactinellida
- Order 1. Hexasterophora (e.g., Euplectella)
- Order 2. Amphidiscophora (e.g., Hyalonema)
Class 3. Demospongiae
- Subclass 1. Tetractinellida
- Order 1. Myxospongida (e.g., Oscarella)
- Order 2. Carnosa (e.g., Chondrilla)
- Order 3. Choristida (e.g., Geodia)
- Subclass 2. Monaxonida
- Order 1. Hadromerina (e.g., Tethya)
- Order 2. Halichondrina (e.g., Halichondria)
- Order 3. Poecilosclerina (e.g., Cladorhiza)
- Order 4. Haplosclerida (e.g., Spongilla)
- Subclass 3. Keratosa (e.g., Euspongia)
Questions and Answers
1. Which is not diploblastic?
a. Nematoda
b. Ctenophora
c. Sponge
d. Cnidaria
Answer: c. Sponge
2. Choanocyte cells are seen in
a. Annelida
b. Porifera
c. Echinodermata
d. Arthropoda
Answer: b. Porifera
3. The spongocoel is covered with
a. Choanocyte
b. Amoebocyte
c. Porocyte
d. Scleroblasts
Answer: a. Choanocyte
