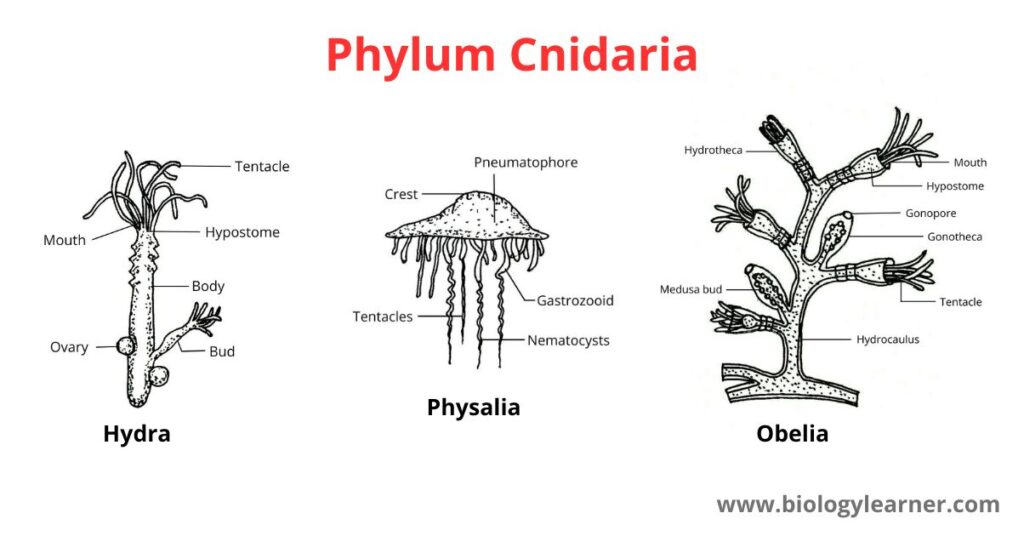
Phylum Cnidaria is the group of multicellular animals belonging to the sub-kingdom of Enterozao. According to tissue differentiation, the animals of this group are two types diploblastic and triploblastic.
In the early days, cnidarians and ctenophores would be considered the animals of a single phylum named Coelenterata.
Hatschek in 1888 separated the Ctenophores from the group Coelenterata. Then the Coelenterata to be divided into two separate phyla – Cnidaria and Ctenophora. In Cnidaria, most animals are marine.
The name Cnidaria is derived from the Greek word Cnidos. “Cnidos = thread”
Cnidaria Definition
Multicellular aquatic animals with diploblastic, coelom free, and containing coelenteron, are called Cnidaria.
Characteristics of Cnidaria
- Their bodies are multicellular and radially symmetrical.
- The animals are diploblastic. The body has two layers called ectoderm and endoderm.
- Like jelly, mesoglea consists of two layers.
- Inside the body is the gastrovascular cavity, called the coelenteron. They are called the Coelenterata because of the presence of the coelenteron.
- They have nematocysts in the cnidoblast cells of the body.
- There is no anus in the body.
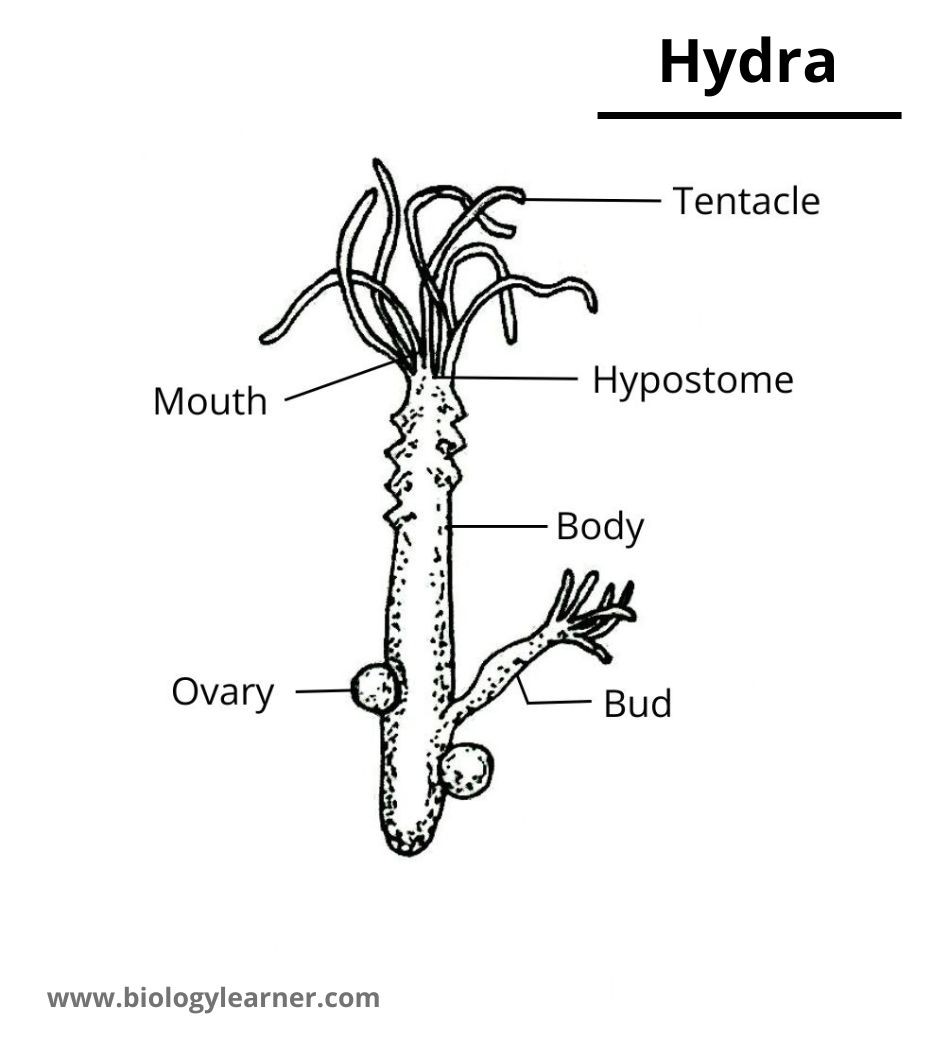
- The oral cavity or hypostome is surrounded by many tentacles.
- Both intracellular and extracellular digestion system is present.
- Alternation of generation are asexual polyploid and sexual medusa may be noticed in the life cycle.
- The planula larva is present in the life cycle.
- The animals of phylum-cnidaria are marine, though some are freshwater form.
Identification Characters
- Tissue layer: Animals in this Phylum have two cell layers(diploblastic) in the embryonic state, e.g., ectoderm and endoderm.
- Body cavity: Gastrovascular cavity or coelenteron present in the body.
- Digestion: Digestion may be intracellular or extracellular.
- Cnidoblast cell: The tentacles contain numerous cnidoblast cells in the animals of the phylum-cnidaria.
- Habitat: The animals are generally marine in this Phylum.
Examples
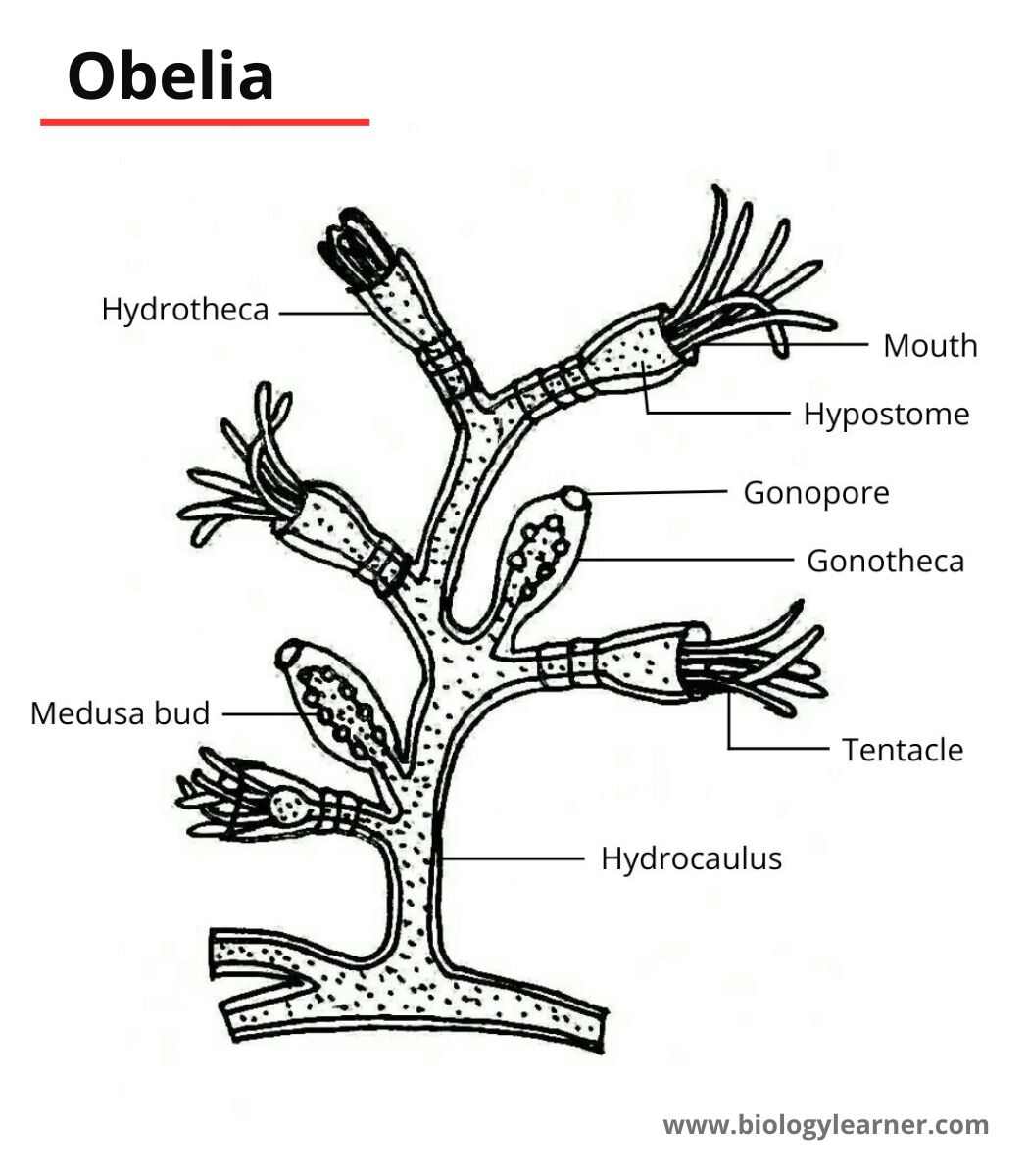
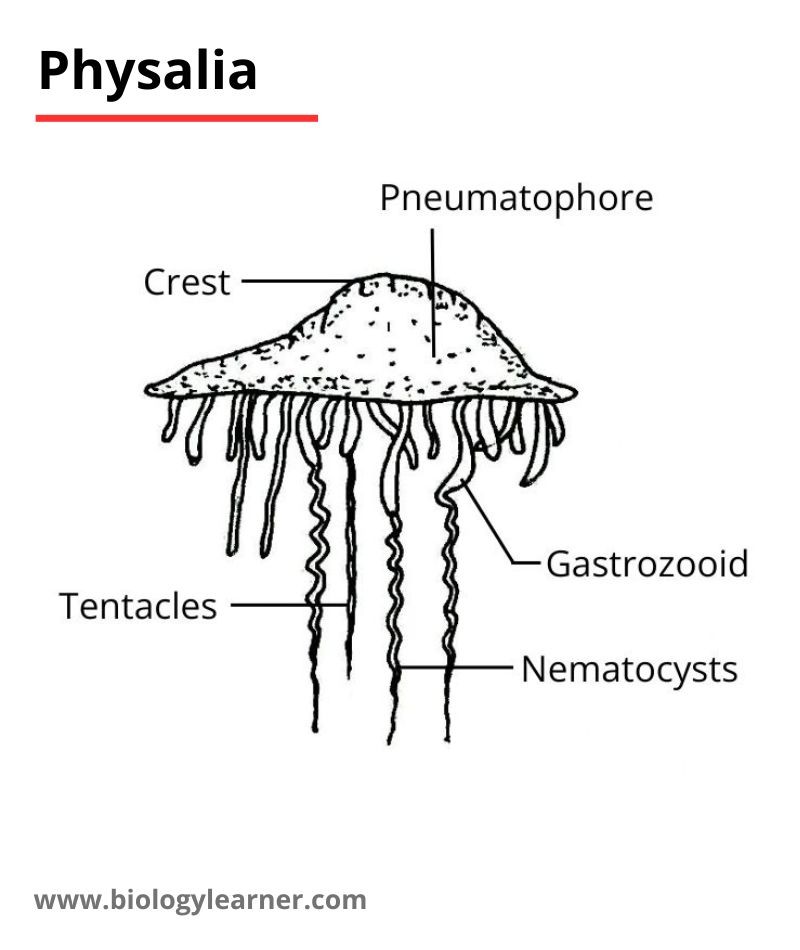
Some common animals of the phylum-cnidaria are Hydra, Aurelia (jellyfish), Obelia, Metridium (Sea anemone), Pennatula, Corallum, Astraea, Gorgonia, etc.
Classification of Cnidaria
Phylum Cnidaria is divided into three classes.
Here, the classification is adopted from Hyman, L.H. (1940). The outline of the classification is given below:
Class 1. Hydrozoa
- Order 1. Hydroida
- Suborder 1. Anthomedusae (e.g., Hydra)
- Suborder 2. Leptomedusae (e.g., Obelia)
- Order 2. Milleporina (e.g., Millepora)
- Order 3. Stylasterina (e.g., Stylaster)
- Order 4. Trachylina
- Suborder 1. Trachymedusae (e.g., Geryonia)
- Suborder 2. Narcomedusae (e.g., Cunina)
- Order 5. Siphonophora
- Suborder 1. Calycophora (e.g., Diphyes)
- Suborder 2. Physophorida (e.g., Physalia)
Class 2. Scyphozoa
- Order 1. Stauromedusae (e.g., Lucernaria)
- Order 2. Cubomedusae (e.g., Tamoya)
- Order 3. Coronate (e.g., Periphylla)
- Order 4. Semaeostomeae (e.g., Aurelia)
- Order 5. Rhizostomae (e.g., Rhizostoma)
Class 3. Anthozoa
- Subclass 1. Octocorallia
- Order 1. Stolonifera (e.g., Clavularia)
- Order 2. Telestacea (e.g., Telesto)
- Order 3. Alcyonacea (e.g., Alcyonium)
- Order 4. Coenothecalia (e.g., Heliopora)
- Order 5. Gorgonacae (e.g., Gorgonia)
- Order 6. Pennatulacea (e.g., Pennatula)
- Subclass 2. Hexacorallia
- Order 1. Actiniaria (e.g., Actinia)
- Order 2. Madreporaria (e.g., Astraea)
- Order 3. Zoanthidea (e.g., Zoanthus)
- Order 4. Antipatharia (e.g., Antipathes)
- Order 5. Ceriantharia (e.g., Cerianthus)
Questions and Answers
1. Nematocysts are a characteristic feature of the phylum
a. Annelida
b. Coelenterata
c. Porifera
d. Echinodermata
Answer: b. Coelenterata
2. In Hydra, the lining of the gastrovascular cavity does not contain
a. Cnidoblasts
b. Sensory cells
c. Interstitial cells
d. None of these
Answer: a. Cnidoblsts
3. Metagenesis is seen in the life cycle of
a. Hydra
b. Sea anemones
c. Aurelia
d. Obelia
Answer: d. Obelia