In the phylum Arthropoda, there is the most number of animal species. The phylum Arthropoda contains more than 1079290 known species like Apis, Laccifer, Millipede, Palaemon, etc.
The name Arthropoda is derived from the Greek words Arthron and podos.
” Arthron = jointed and Podos = foot “
The animals of this phylum have a haemocoelomic body cavity and jointed legs. In 1848, Leuckart who was separated arthropods as a distinct phylum. But Van Siebold coined the term Arthropoda in the same year.
Definition of Arthropoda
Phylum Arthropoda is a group of organisms having a bilaterally symmetrical and metamerically segmented body with jointed appendages containing a chitinous exoskeleton, haemocoelomic body cavity, and ganglionated nerve cords.
Characteristics of Arthropoda
- Bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, and metamerically segmented body.
- The body is divided into two or three parts.
- Presence of chitinous cuticle as an exoskeleton.
- Haemocoel or coelom (filled with blood) is present in the body cavity.
- A complete and complex alimentary canal is present.
- The mouth and anus are located at opposite ends of the body.
- Presence of a pair of jointed appendages in each body segment.
- Mouth with distinct mouthparts.
- Respiration occurs through the trachea, book gill, or book lung.
- Open type circulatory system is present.
- Their excretory organs are the green gland (Prawn), malpighian tubules (Insects), or coxal gland ( Spiders, Scorpion).
- The endocrine system is present in the body.
- The nervous system contains ganglionated ventral nerve cords and cerebral ganglia.
- Sense organs are generally compound eyes (Insects), simple eyes (Spiders), or statocysts (Prawn).
- They are generally unisexual. Sexual dimorphism is prominent.
Identification Characters
- Appendages: The body is segmented. Each body segment contains a pair of jointed appendages.
- Exoskeleton: Exoskeleton is covered with chitin.
- Excretory organs: Excretory organ represents green gland or malpighian tubules.
- Body cavity: The body provided with reduced coelom and coelom remains filled with blood (Haemocoel).
- Respiratory organs: Respiratory organs are the trachea, book lung, and book gill.
Examples
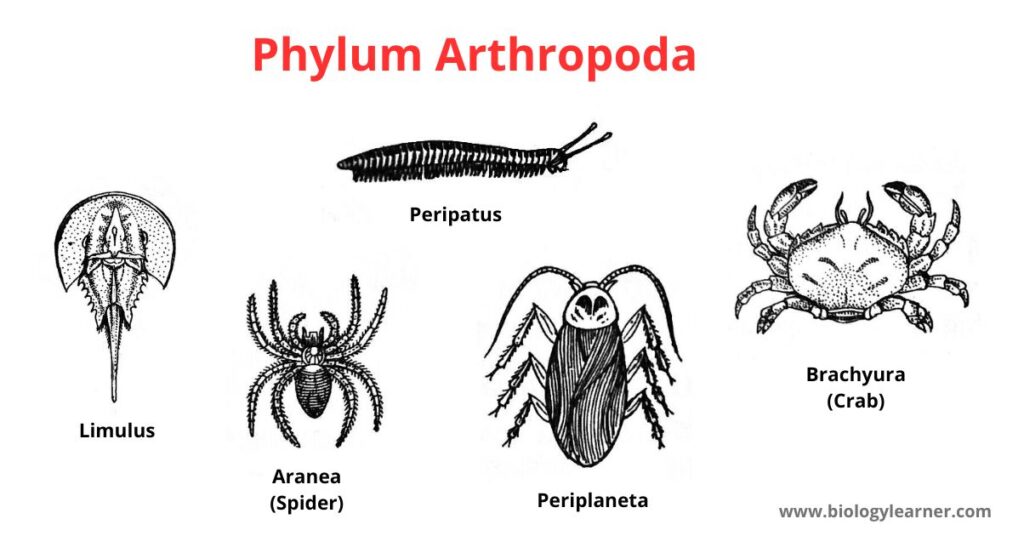
Some common Arthropods are Limulus, Peripatus, Julus, Lepsima, Periplaneta, Musca, Seylla, Nephila, Scolopendra, etc.
