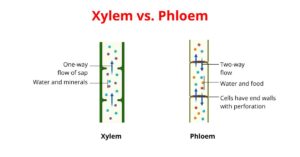
Xylem vs. Phloem: 15 Major Differences, Examples
Xylem and phloem are the complex tissues. They constitute the component parts of the vascular bundles. They both have distinct functions and characteristics. Xylem Xylem is a vascular tissue that…
Biology is a vast discipline that deals with the study of life and living organisms, including their origins, structure, physiology, evolution, behavior, distribution, and taxonomy.

Xylem and phloem are the complex tissues. They constitute the component parts of the vascular bundles. They both have distinct functions and characteristics. Xylem Xylem is a vascular tissue that…
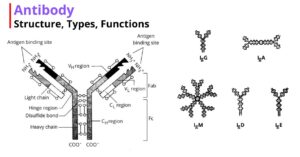
Antibodies are the proteins produced by the B-lymphocytes in response to the antigen or foreign bodies. Structure of Antibody IgG is the most studied immunoglobulin and serves as a model…

Acquired immunity does not occur unless foreign microbes or toxins enter the body. Each microbe or toxin contains one or more specific chemical substances that play an important role in…
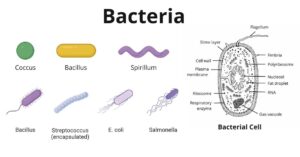
Bacteria exert both deleterious and benefical effects on human life. Beneficial species liberate fertilizer elements for growing crops, destroy sewage and other wastes, and produce valuable chemicals. Some species are…
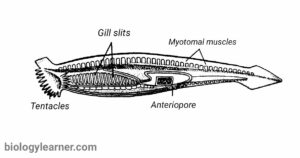
Cephalochordata (Gr., kephale, head; chorde, cord) is a sub-phylum within the phylum Chordata. The animals in this group are small, marine invertebrates. They are commonly called lancelets or amphioxi. Cephalochordates…

The sub-phylum Urochordata (Gr., uro, tail; chorde, cord) is a part of the phylum Chordata. The animals in this group are called sea squirts,or tunicates. These animals are very unique…

Phylum Hemichordata is generally considered the sister group of the phylum Echinodermata. The animals are marine deuterostomes. They are more or less worm-like, having the ancestral tripartite body of proboscis,…

Chloroplasts are double membraned rod-like oval or spherical cell organelles in the cytoplasm of most plant cells that help in photosynthesis. It is a green plastid containing chlorophylls. Animal cells…

Mitochondria are the rod-shaped, ovoid, or thread-like, scattered minute particles in all aerobic cells of higher animals and plants. These are also present in algae, protozoa, and fungi. Bacterial cells,…
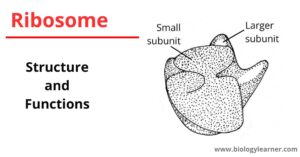
Ribosomes are membraneless, small, sub-spherical ribonucleoprotein particles. They are often found connected to the outside of the endoplasmic reticulum and nucleus. Ribosomes also occur freely in the cytoplasm (cytoplasmic matrix),…