
Evolution of Sporophyte in Bryophytes
The evolution of sporophyte in Bryophytes have been explained with the help of two theories: one is the Antithetic Theory or Theory of Sterilization and the other one is the…
Botany is the branch of biology that deals with the study of plants, including their structure, physiology, reproduction, and biochemical processes.
Botany is a very vast and comprehensive science and is divided into various major branches such as morphology, histology, physiology, plant anatomy, genetics, cytology, taxonomy, ecology, paleobotany, plant geography, etc.
The scope of botany and its consequent importance is vast and immense. For the very existence of not only human beings but also all animals, plants are necessary.
The study of botany forms a necessary informational background for students preparing for careers in agriculture, horticulture, forestry, bacteriology, pharmacology, soil conservation, and other related fields.

The evolution of sporophyte in Bryophytes have been explained with the help of two theories: one is the Antithetic Theory or Theory of Sterilization and the other one is the…

Jungermanniales is the largest order of class Hepaticopsida in the division Bryophyta. Characteristics of Jungermanniales Structure of Gametophyte in Jungermanniales The plant body is gametophytic. The gametophytes are thalloid, except…

Marchantiales is an order of Division Bryophyta (Class Hepaticopsida). Structure of Gametophyte The gametophyte of Marchantiales is the plant body. External Morphology Internal Morphology Sexual Reproductive Structures of Marchantiales Antheridium…

Sterilization is the complete eradication of microorganisms (fungi, bacteria, and viruses) present on the surface of any material. The microorganisms can be removed or destroyed from the definite materials (seeds,…
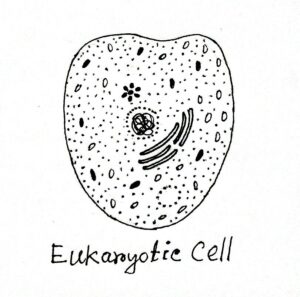
The Eukaryotic cell is the most advanced type of cell which is present in both animals and plants. Dougherty (1957) has divided cells into two types (based on the organization…

Viroids are the group of pathogens of some higher plants. Theodor Otto Diener introduced the viroid in 1971 for a new group of sub-viral plant pathogens. He was the first…

In 1957 Dougherty has divided cells into two types based on the organization in the nucleus of the cell. One is a prokaryotic cell (primitive cell) and the other is…

Bacteria are unicellular. Their structure is a very simple type. Bacteria are prokaryotes because they do not have a well-formed nucleus. A typical bacterial cell is structurally very similar to…
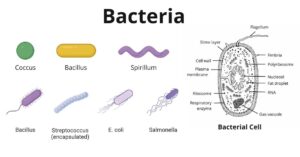
Bacteria are a type of simple, microscopic, unicellular organism. In 1675, Dutch scientist A. van Leeuwenhoek was first discovered bacteria. He proved the existence of bacteria in his own made…

In 1822, the scientist Goldfuss first used the term protozoa. Protozoa are referred to as animals whose bodies are made up of a single cell. However, it represents a division…