DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) isolation is the process by which DNA is extracted from proteins, membranes, and other cellular materials contained in the cell.
In Eukaryotic cells (Human, plant, and animal cells), DNA is organized as chromosomes in the nucleus.
Objective
Isolation of Eukaryotic DNA from tissues of a plant using the CTAB (cetyltrimethylammonium bromide) method.
Principle of Isolation of Eukaryotic DNA
DNA is a high molecular weight macromolecule, organized as chromosomes mainly in a eukaryotic cell organelle called a nucleus. Several methods are used for the isolation of eukaryotic DNA from tissues of organisms such as humans, plants, and animals.
Although, isolation of quality DNA from plants (mainly alkaloid-yielding plants) is rather difficult(due to the low yield of DNA high amount of plant tissues is required). The cesium chloride (CsCl) gradient method is expensive and time-consuming.
Therefore, the Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) method is commonly used due to the less expensive and high yield of eukaryotic DNA.
Requirements for Isolation of Eukaryotic DNA
- Water bath incubator (60°C), refrigerated high-speed centrifuge
- Plant leaves (as per desire and availability), mortar, and pestle.
- Isopropanol and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB)
Reagents
- Chloroform: isoamyl alcohol (24:1, v/v) (prepare fresh and keep in a dark bottle)
- 7.5 M ammonium acetate (57.8 g/100 me, pH- 7.7)
- RNase (10 mg/ml with distilled water) or TE buffer (store in -20°C) [Tris-EDAT buffer (TE buffer)] [Tris-HCL 10mM (pH- 7.4) and EDTA 1mM (pH- 8.0)]
- 10mM ammonium acetate (0.0771 g/100ml, pH- 7.7 autoclave and store in refrigerator)
- 70% Ethyl alcohol (ethanol)
Preparation of isolation buffer
- 10 mM Tris-HCL (1 M stock solution, 12.11 g/100 ml, pH- 8.0)
- (v/v) mercapteoethanal solution (should be added freshly)
- M NaCl (29.22 g dissolve in 100ml to get 5 M stock solution)
- mM EDTA (18.62 g/100 ml, pH-8.0, 0.5 M stock solution)
- w/v CTAB (20 g/100 ml to get 20% stock solution)
Mix these chemicals fresh in a proper ratio and prepare an isolation buffer. For making a 10 ml isolation buffer mix these stock solutions in the following:
- 10 mM Tris-HCL- 0.1 ml
- 0.2% (v/v) mercapto-ethanol (fresh)- 0.02 ml
- 1.4 M NaCl- 2.8 ml
- 20 mM EDTA- 0.4 ml
- 2% w/v CTAB- 1 ml
Procedure
- Collect fresh plant tissue, weigh 1.0 g, and grind in liquid nitrogen to make powder or paste keeping in a pre-chilled pestle and mortar (liquid nitrogen may also be used). The plant tissues should not have been ground earlier.
- Warm 10 ml isolation buffer in a centrifuge tube at 60°-65°C in a water bath.
- Mix paste or powder of tissue in preheated isolation buffer. Incubate at 65°C in a water bath with gentle swirling.
- Extract with equal volume (24:1) of chloroform and isoamyl alcohol and then mix gently.
- Centrifuge at 10000 rpm for 20-25 minutes at room temperature.
- Collect the clear aqueous phase (supernatant) very carefully using a wide bore pipette in a fresh centrifuge tube. Note the volume of the aqueous phase (the same process of chloroform and isoamyl alcohol extraction is repeated if the supernatant is not clear.
- Gently add 2/3 volume of isopropanol to the aqueous phase and mix properly (the fibers of nucleic acid become visible).
- Then centrifuge immediately for 10-15 minutes at 10000 rpm.
- Remove the aqueous phase and collect over tissue paper so that isopropanol could be removed.
- Wash the pellet twice with 70% ethanol centrifuging at 6000 rpm for 5 minutes at room temperature.
- Dry the plates at 35°C for 30 minutes till completely dried.
- Pour 100-200 ml TE buffer (for DNA isolation about 100 ml for 1 g tissue) or sterile distilled water so that the pellets could be dissolved. Add 10 ml RNase from the stock solution (10 mg/ml). Incubate for 30-60 minutes at 35°C.
- Then add 2 ml of TE buffer or sterile distilled water to dilute the sample. Gently add 7.5 M ammonium acetate to get the final concentration of 2.5 M. Also adds 2.5 ml of cold ethanol for precipitating the DNA.
- Incubate it overnight at -20°C (deep freeze) and centrifuge DNA at 10000 rpm for 15 minutes at 4°C.
- Dry the pellets in the air and re-suspended them in 100-150 ml sterile distilled water or TE buffer.
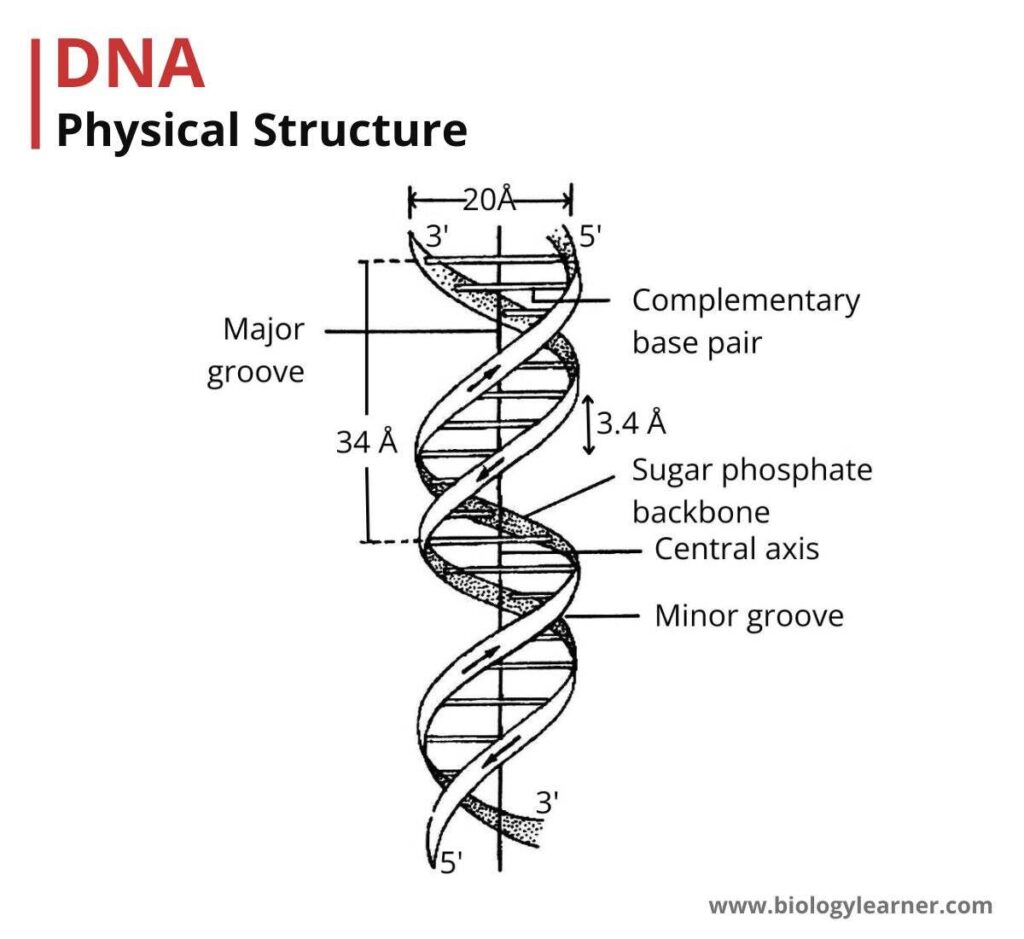
Results
A white or milky precipitate of DNA will be observed on the sides or bottom of centrifuge tubes after precipitating with iso-propanol and congratulation.
Precautions
- EDTA, NaCl, CTAB, Tris-HCL, and ammonium acetate should be autoclaved.
- All glassware should be autoclaved.
- Chloroform: isoamyl alcohol (24:1) should be freshly prepared and stored in a dark bottle.
