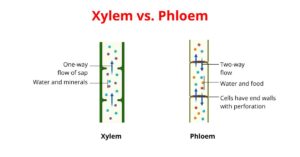
Xylem vs. Phloem: 15 Major Differences, Examples
Xylem and phloem are the complex tissues. They constitute the component parts of the vascular bundles. They both have distinct functions and characteristics. Xylem Xylem is a vascular tissue that…

Xylem and phloem are the complex tissues. They constitute the component parts of the vascular bundles. They both have distinct functions and characteristics. Xylem Xylem is a vascular tissue that…
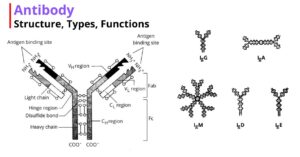
Antibodies are the proteins produced by the B-lymphocytes in response to the antigen or foreign bodies. Structure of Antibody IgG is the most studied immunoglobulin and serves as a model…

Acquired immunity does not occur unless foreign microbes or toxins enter the body. Each microbe or toxin contains one or more specific chemical substances that play an important role in…

Gnetales is an order of the gymnospermic seed plants. This order is composed of three genera- Gnetum, Ephedra, and Welwitschia. Chamberlain (1935) has placed all three genera in a single-family…
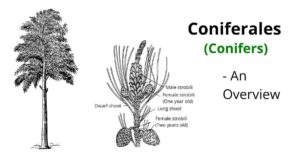
Coniferales is a group of gymnospermic plants. The members of this group form the common conifers. It includes both fossil and present-day living genera. Coniferales reached their maximum development probably…

Ginkgoales is a gymnospermic order having one living genus (Ginkgo biloba). The members of this order once had an almost worldwide distribution in the Jurassic period. The fossil members of…
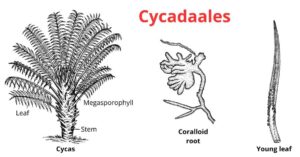
Cycadales is a gymnospermic order. Members of this order are mostly inhabitants of tropical and subtropical regions. It includes both living and fossil genera. They originated in the Mesozoic era…
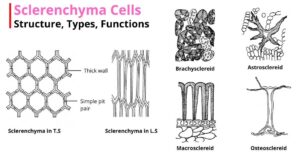
Sclerenchyma is a type of simple permanent tissue that provides structural support to the plant. It consists of thick-walled, lignified sclerenchyma cells. The cells mostly lack protoplasm at maturity and…
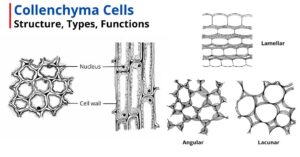
Collenchyma is a simple permanent tissue composed of living cells with thickened walls. It is a part of the ground tissue and provides support and mechanical strength to the newly…
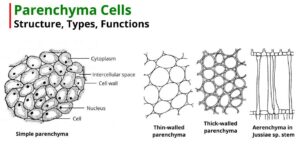
Parenchyma is a simple permanent tissue that makes up large portions of various plant organs. It consists of thin-walled living parenchymatous cells. The word parenchyma comes from the Greek words…