Xylem and phloem are the complex tissues. They constitute the component parts of the vascular bundles. Xylem and phloem both have distinct functions and characteristics.
Xylem
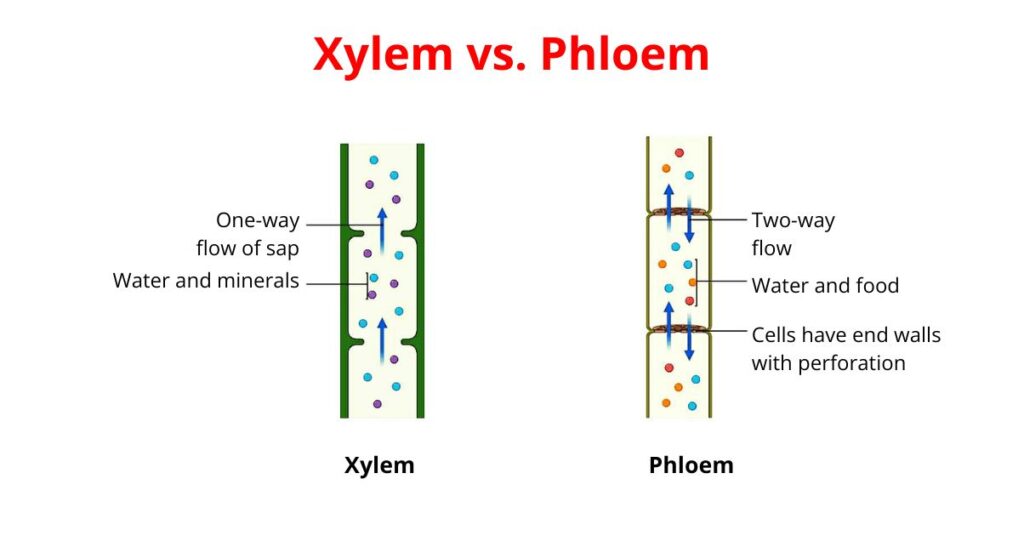
Xylem is a vascular tissue that transports water and solutes from the root to the leaves and other parts of the plant.
Kay features of xylem are as follows:
- The word xylem comes from the Greek word xylon, which means wood. As most of the xylem tissues are found in the woody part of the stem.
- Xylem tissue exhibits a star-like appearance under a microscope.
- It is present at the center of the vascular bundle, and the total amount is much more than the phloem.
- Xylem is composed of several different types of cells, such as vessels, tracheids, xylem fibers, and xylem parenchyma.
- These cells are mostly dead cells. Lignin is present in the cell walls, which provide mechanical support to the plants.
- Initially, xylem occurs in the apical meristem, and it is called primary xylem. Later, secondary xylem develops as a ring around the primary xylem in woody plants.
- In mature woody plants, the wood, i.e., xylem, is differentiated into heartwood and sapwood. The heartwood represents the primary xylem that provides physical support, and the sapwood represents the secondary xylem that conducts water and minerals.
- Transport in xylem is a passive process where no energy is required.
- The primary function of xylem tissue is to conduct water and minerals and provide mechanical strength to the plants.
Phloem
Phloem is the vascular tissue that transports organic compounds (produced during photosynthesis) throughout the plant.
- The word phloem is derived from the Greek word phloios, which means bark. As the phloem tissue forms most of the parts of bark in plants.
- Phloem is found towards the periphery of the vascular bundle, and the total amount is less than the xylem.
- Phloem tissue is composed of many types of cells, such as sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibers, and phloem parenchyma.
- These cells are mostly living cells and are not lignified, i.e., lignin is not present in the cell walls.
- Primary phloem develops from the apical meristem in the root and shoot.
- The primary function of phloem tissue is to transport organic food from leaves to other parts of the plant. The transport is bidirectional, and the food can move both up and down in the plant.
- Unlike xylem, transport in phloem is an active process where energy is required for the conduction of the food.
Important Differences (Xylem vs. Phloem)
| Basis for Comparison | Xylem | Phloem |
| Definition | Xylem is a vascular tissue that transports water and solutes from the root to the leaves and other parts of the plant. | Phloem is the vascular tissue that transports organic compounds (produced during photosynthesis) throughout the plant. |
| Terms | The word xylem comes from the Greek word xylon, which means wood. As most of the xylem tissues are found in the woody part of the stem. | The word phloem is derived from the Greek word phloios, which means bark. As the phloem tissue forms most of the parts of bark in plants. |
| Location | Xylem is usually found in the center of the vascular bundle. | Phloem is mainly situated towards the periphery of the vascular bundle. |
| Found in | Xylem tissues are found in roots, stems, and leaves. | Phloem tissues are found in stems and leaves and later form in the roots, fruits, and seeds. |
| Plant body Formation | Xylem forms most parts of the wood of the plant body. | Phloem forms most parts of the bark of the plant body. |
| Components | Xylem is composed of vessels, tracheids, xylem fibres, and xylem parenchyma. | Phloem is made up of sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibers, and phloem parenchyma. |
| Types of Fibers | Xylem fibers are much long and stronger. | Phloem fibers are short but flexible. |
| Nature of Cells | The cells of the xylem are dead cells except for the xylem parenchyma. | The cells of the phloem are living cells except for the phloem fibers. |
| Cell Walls | The cell walls are thick, and some of them are lignified. | The cell walls are thin, but no lignin is present. |
| Tyloses Formation | Tyloses are formed in the xylem tissue. | Tylose is not formed in the phloem tissue. |
| No. of Tissues | The total amount of xylem tissue in the vascular bundle is more than the phloem tissue. | The total amount of phloem tissue in the vascular bundle is less. |
| Conductive Elements | Two types of conductive elements are present in xylem: vessels and tracheids (consists of dead cells). | Only one type of conductive element, i.e., sieve tube, is present in phloem (consists of living cells). |
| Differentiation | Xylem can show differentiation. In mature plants, it differentiated heartwood and sapwood. | There is no such differentiation seen in phloem. |
| Functions | The main function of xylem tissue is to transport water and minerals from the root to leaves and other parts of the plant. It also provides mechanical support to the plant. | The main function of phloem is to transport food and other nutrients from the leaves to different parts of the plant. Although it has no mechanical function. |
| Direction of Transport | The transport through xylem is unidirectional. The water and minerals are only moved up from the root. | The transport through phloem is bidirectional. The food and nutrients can conduct both up and down in the plant. |

Pretty great post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wished to
mention that I’ve truly loved surfing around your weblog posts.
After all I’ll be subscribing on your feed and I hope you write once more soon!